大浩浩的笔记课堂——FRM考试学习笔记127
- 2026-02-16 00:13:31
Topic 56 Introduction of Basel Accord
1.Basic terms:
⑴economic capital:
It is an internal policy decision by senior management and the board.
⑵regulatory capital:
①definition:
It is the rule based with the intention to ensure enough capital that is in the banking system.
②motive:
It has a macro-prudential motive.
⑶risk-weighted assets(RWA):
①definition:
They are bank´s assets weighted according to risk.
②formula:
RWA=RW×NP
⑷loss:
①expected loss(EL):
其用reserve来覆盖预期损失。
②unexpected loss(UL):
其用capital来覆盖非预期损失。
③超过容忍水平的潜在损失
2.Evolution of Basel Accord:
⑴prior to 1988:
①Bank capital regulations were inconsistent across countries.
②Bank capital regulations ignored the riskiness of individual banks.
⑵1988 Basel Ⅰ:
①Strengthen and standardize the global banking system.
②Set capital charges against credit risk.
⑶1996 Amendment:
Add capital adequacy requirements against market risk.
⑷2004 Basel Ⅱ:
Create more risk-sensitive capital requirements and add a charge against operational risk.
⑸Basel Ⅲ:
①raising capital standards
②requiring a leverage ratio
③instituting a global liquidity standard
3.The 1988 Basel Ⅰ:
⑴capital requirement:
①The bank´s total assets to capital ratio had to be less than 20,or the capital to total assets had to be greater than 5%.
②To keep capital equal to at least 8% of the risk-weighted assets:
A.tier 1 capital(at least 4%):
a/ equity(at least 2%)
b/ noncumulative perpetual preferred stock
·特别注意!
·Goodwill is subtracted from equity.
B.tier 2 capital(supplementary capital):
a/ cumulative perpetual preferred stock
b/ certain types of 99-year debenture issues
c/ subordinated debt with an original life of more than 5 years
⑵Cooke ratio:
①The credit risk exposures can be divided into 3 categories:
A.those arising from on-balance-sheet assets(excluding derivatives):
The risk weight in this layer is:
a/ 0%:
cash,gold bullion,Treasury bonds or insured residential mortgages
b/ 20%:
claims on OECD banks,securities issued by U.S. government agencies,claims on municipalities
c/ 50%:
uninsured residential mortgage loans or derivatives
d/ 100%:
corporate bonds/loans,less-developed country debt
B.those arising for off-balance sheet terms:
To account for off-balance-sheet items,such as guarantees,letter of credit,credit lines,the Basel Accord computes a credit exposure that is equivalent to the notional for a loan,through credit conversion factors.
C.those arising form over-the-counter derivatives:
Other derivatives are given special treatment due to the complexity of their exposures:
max(V,0)+a×L
a/ V:the current value of the derivative to the bank
b/ a:add-in factor
c/ L:principal amount
·特别注意!
·The credit equivalent amount arising from the second or third category of exposures is multiplied by the risk weight for the counterparty in order to calculate the risk-weighted assets.
·The risk weights are similar to those in first category,except that the risk weight for a corporation is 0.5 and the risk weight for OECD banks is 0.2.
②The total risk-weighted assets for a bank with N on-balance-sheet items,and M off-balance-sheet items:

⑶major limitations:
①All corporate loans were treated the same regardless of the
creditworthiness of the borrower.
②It also ignored the benefits of diversification,did not include a model of default correlation.
4.The 1995 netting:
⑴With netting,the exposure is the payoff from a option on a portfolio:

⑵Without netting,the exposure is the payoff from a portfolio of options:

⑶1995,netting had been successfully tested:

5.The 1996 amendment:
⑴the formula:
①1-day,99%:
max(VaRt-1,mc×VaRavg)+SRC
A.t-1:the precious day
B.mc:multiplicative factor,最小值为3
C.VaRavg:average over the past 60 days
D.SRC:specific risk charge
②10-day,99%:
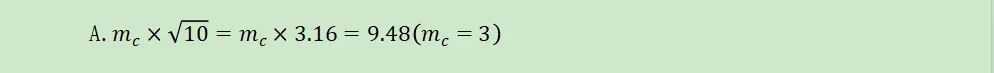
B.9.48×average 1-day VaR
③total capital:
Total capital=(credit risk RWA+market risk RWA+operational risk RWA)×8%
⑵back-testing:
①An exception occurs if the day´s change in value exceeded the VaR estimate of the precious day.
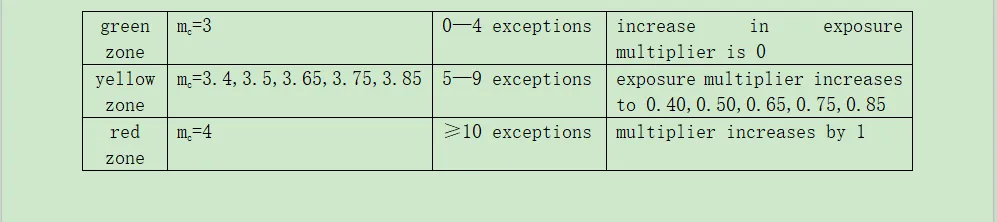
②When backtesting VaR,the number of exceptions is determined for a 250-day testing period.Based on the number of exceptions,the bank´s exposure is categorized into one of three zones and VaR is scaled up by the appropriate multiplier(subject to a floor of mc=3):
大浩浩的笔记课堂之FRM考试学习笔记合集
【正文内容】
FRM二级考试
A.Market Risk
A.市场风险
Topic 1 Estimating Market Risk Measures:An Introduction and Overview
Topic 2 Non-Parametric Approaches
Topic 3 Parametric Approaches:Extreme Value
Topic 6 Messages from the Academic Literature on Risk Management for the Trading Book
Topic 7 Some Correlation Basics:Properties,Motivation and Terminology
Topic 8 Empirical Properties of Correlation:How Do Correlation Behave in the Real World
Topic 9 Statistical Correlation Models—Can We Apply Them to Finance
Topic 10 Financial Correlation Modeling—Copula Correlations
Topic 11 Empirical Approaches to Risk Metrics and Hedging
Topic 12 The Science of Term Structure Models
Topic 13 The Shape of the Term Structure
Topic 14 The Art of Term Structure Models:Drift
Topic 15 The Art of Term Structure Models:Volatility and Distribution
Topic 16 Overnight Index Swap(OIS) Discounting
B.Credit Risk
B.信用风险
Topic 20 Default Risk:Quantitative Methodologies
Topic 21 Credit Risks and Credit Derivatives
Topic 22 Credit and Counterparty Risk
Topic 23 Spread Risk and Default Intensity Models
Topic 25 Structured Credit Risk
Topic 26 Defining Counterparty Credit Risk
Topic 27 The Evolution of Stress Testing Counterparty Exposures
Topic 28 Netting,Compression,Resets,and Termination Features
Topic 32 Default Probability,Credit Spreads and Credit Derivatives
Topic 33 Credit Value Adjustment(CVA)
Topic 35 Credit Scoring and Retail Credit Risk Management
Topic 38 Understanding the Securitization of Subprime Mortgage Credit
C.Operational Risk
C.操作风险
Topic 39 Principles for the Sound Management of Operational Risk
Topic 40 Enterprise Risk Management:Theory and Practice
Topic 41 Observations on Developments in Risk Appetite Frameworks and IT Infrastructure
Topic 42 Operational Risk Data and Governance
Topic 45 Validating Rating Models
Topic 47 Risk Capital Attribution and Risk-Adjusted Performance Measurement
Topic 48 Range of Practices and Issues in Economic Capital Framework
Topic 49 Capital Planning at Large Bank Holding Companies
Topic 50 Repurchase Agreements and Financing
Topic 51 Assessing the Quality of Risk Measures
Topic 52 Estimating Liquidity Risks
Topic 53 Liquidity and Leverage
Topic 54 The Failure Mechanics of Dealer Banks
