神经网络激活函数完整指南
1. 什么是激活函数
激活函数(Activation Function)是神经网络中的核心组件,它决定了神经元是否应该被"激活"。没有激活函数,神经网络只能学习线性关系,即使堆叠多层也等价于单层线性变换。
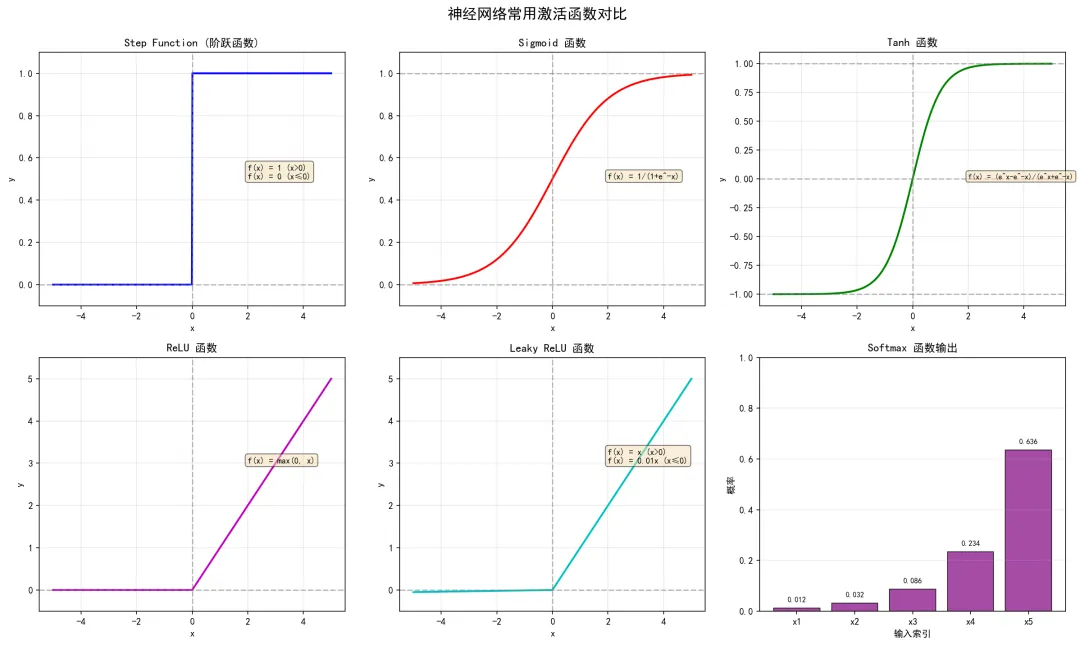 激活函数总览
激活函数总览1.1 激活函数的作用
1.2 数学定义
激活函数本质是一个非线性函数 f(x):
其中:
2. 常用激活函数详解
2.1 Step Function(阶跃函数)
最简单的激活函数,模拟生物神经元的"全有或全无"特性。
数学公式:
代码实现:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
defstep_function(x):
return np.array(x > 0, dtype=int)
x = np.arange(-5.0, 5.0, 0.1)
y = step_function(x)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.show()
特点:
应用场景: 早期感知机模型,现在很少使用
2.2 Sigmoid 函数
Sigmoid 是最常用的激活函数之一,将输出映射到(0,1)区间。
数学公式:
代码实现:
defsigmoid(x):
return1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
# 测试
print(sigmoid(0)) # 0.5
print(sigmoid(3.14)) # 约 0.96
特点:
梯度消失演示:
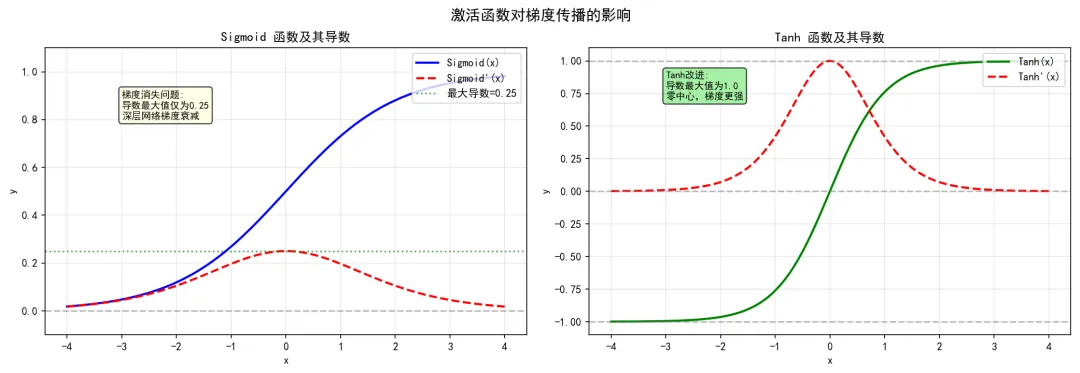 梯度对比
梯度对比注意:当使用Sigmoid作为激活函数时,深层网络的梯度会逐层衰减,导致靠近输入层的权重几乎无法更新。
2.3 Tanh 函数
双曲正切函数,是Sigmoid的零中心版本。
数学公式:
代码实现:
deftanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
# 或直接使用 numpy
# y = np.tanh(x)
特点:
与Sigmoid对比:
2.4 ReLU 函数
Rectified Linear Unit(修正线性单元),目前最常用的隐藏层激活函数。
数学公式:
代码实现:
defrelu(x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
特点:
- • ❌ Dying ReLU问题:负区间梯度为0,可能导致神经元"死亡"
Dying ReLU示意:
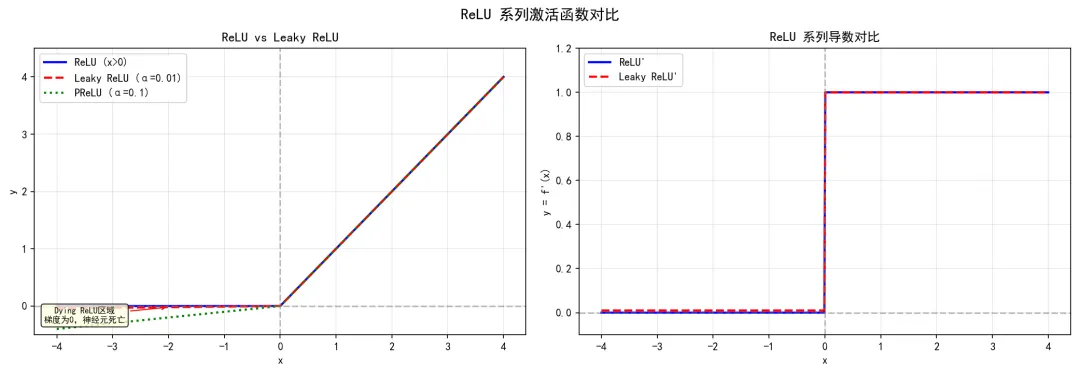 ReLU对比
ReLU对比
2.5 Leaky ReLU
ReLU的改进版本,解决Dying ReLU问题。
数学公式:
其中 通常取0.01。
代码实现:
defleaky_relu(x, alpha=0.01):
return np.where(x > 0, x, alpha * x)
特点:
2.6 Softmax 函数
Softmax用于多分类问题的输出层,将输出转换为概率分布。
数学公式:
代码实现:
defsoftmax(x):
"""计算softmax,防止数值溢出"""
max_x = np.max(x) # 减去最大值防止溢出
exp_x = np.exp(x - max_x)
return exp_x / np.sum(exp_x)
# 示例
inputs = [0.3, 2.9, 4.0]
print(softmax(inputs)) # 输出概率分布
特点:
3. 激活函数在神经网络中的应用
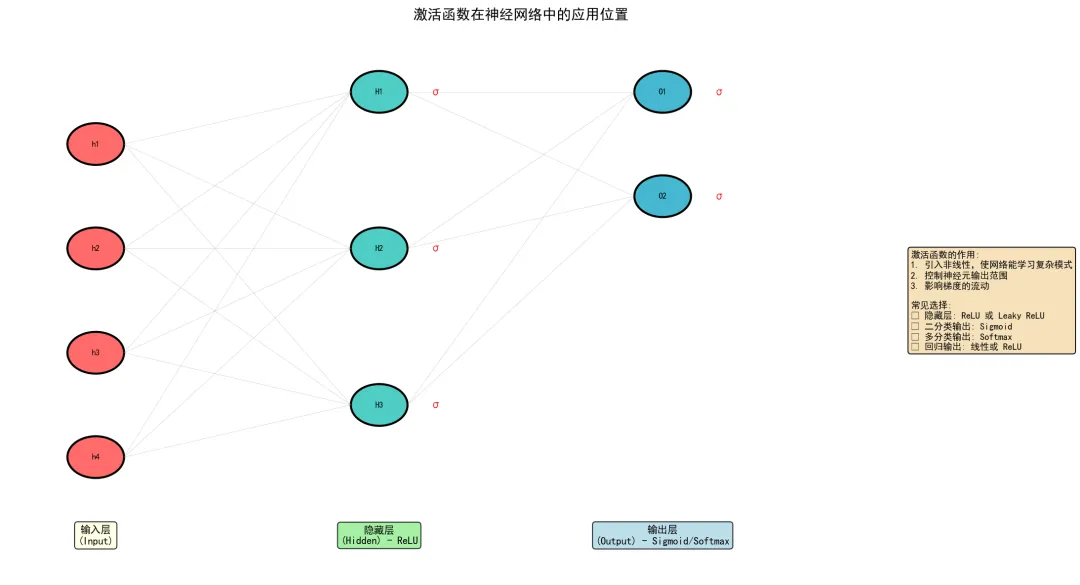 神经网络中的应用位置
神经网络中的应用位置3.1 常见配置
3.2 代码示例
import numpy as np
classNeuralNetwork:
def__init__(self, layer_sizes):
"""
创建一个多层神经网络
layer_sizes: [输入层, 隐藏层1, 隐藏层2, ..., 输出层]
"""
self.weights = []
self.biases = []
# 初始化权重和偏置
for i inrange(len(layer_sizes) - 1):
w = np.random.randn(layer_sizes[i], layer_sizes[i+1]) * 0.01
b = np.zeros((1, layer_sizes[i+1]))
self.weights.append(w)
self.biases.append(b)
defrelu(self, x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
defsigmoid(self, x):
return1 / (1 + np.exp(-np.clip(x, -500, 500)))
defsoftmax(self, x):
exp_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x, axis=1, keepdims=True))
return exp_x / np.sum(exp_x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
defforward(self, X):
"""前向传播"""
self.activations = [X]
for i inrange(len(self.weights) - 1):
z = np.dot(self.activations[-1], self.weights[i]) + self.biases[i]
a = self.relu(z) # 隐藏层用ReLU
self.activations.append(a)
# 输出层
z_out = np.dot(self.activations[-1], self.weights[-1]) + self.biases[-1]
output = self.softmax(z_out) # 多分类用Softmax
return output
# 使用示例
nn = NeuralNetwork([784, 256, 128, 10]) # MNIST网络结构
4. 梯度消失问题详解
4.1 问题本质
在反向传播中,梯度需要逐层传递回输入层:
如果激活函数的导数 ,则梯度会指数级衰减。
4.2 各函数梯度对比
4.3 解决方案
- 2. Batch Normalization - 稳定每层输入分布
- 3. 残差连接(ResNet) - 提供梯度直接通道
5. 激活函数选择指南
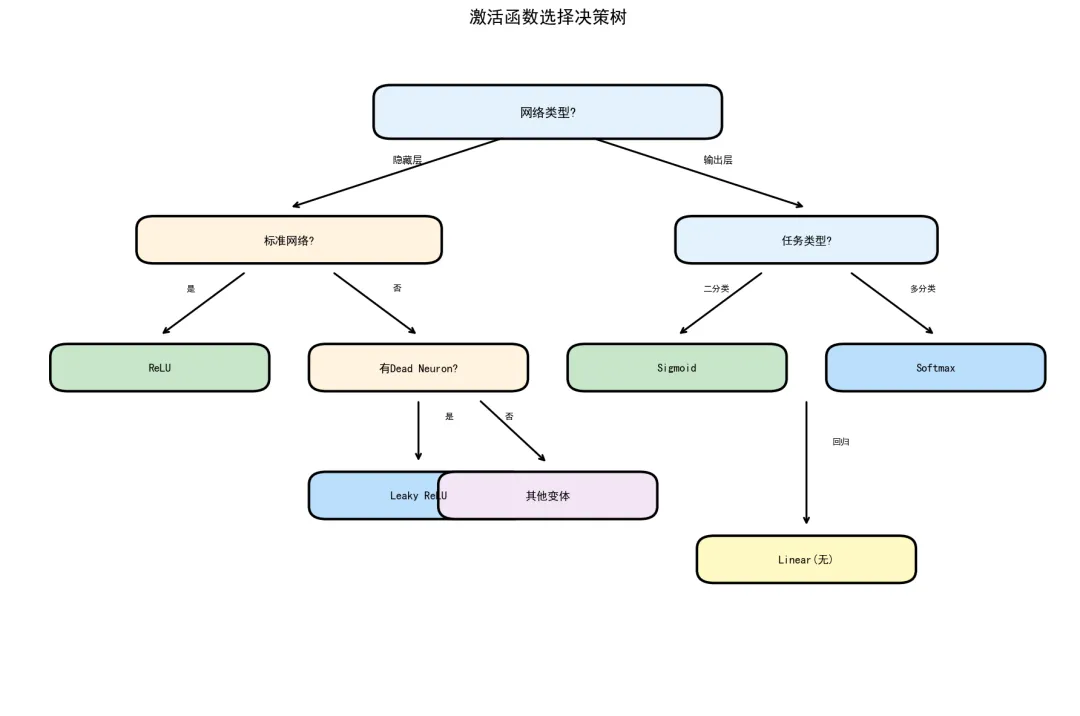 选择指南
选择指南5.1 决策流程
1. 网络类型是什么?
├── 隐藏层 → 使用 ReLU 或 Leaky ReLU
└── 输出层 → 根据任务类型选择
├── 二分类 → Sigmoid
├── 多分类 → Softmax
└── 回归 → Linear(无激活)
2. 是否遇到Dying ReLU?
├── 是 → 改用 Leaky ReLU / PReLU / ELU
└── 否 → 继续使用 ReLU
3. 是否需要输出概率?
├── 是 → Sigmoid 或 Softmax
└── 否 → ReLU / Tanh / Linear
5.2 实践建议
初学者建议配置:
# 推荐配置
hidden_activation = 'relu'# 隐藏层
output_activation = 'softmax'# 多分类
# 或
output_activation = 'sigmoid'# 二分类
调参建议:
- • 如果准确率突然下降,检查是否有Dying ReLU
- • 尝试Leaky ReLU(α=0.01~0.3)
6. 代码演示
6.1 独立函数测试
# 独立测试各激活函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义激活函数
defstep_function(x):
return np.array(x > 0, dtype=int)
defsigmoid(x):
return1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
deftanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
defrelu(x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
defleaky_relu(x, alpha=0.01):
return np.where(x > 0, x, alpha * x)
defsoftmax(x):
exp_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x))
return exp_x / np.sum(exp_x)
# 测试数据
x = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100)
# 绘制对比图
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(15, 10))
functions = [
('Step', step_function),
('Sigmoid', sigmoid),
('Tanh', tanh),
('ReLU', relu),
('Leaky ReLU', leaky_relu),
]
for ax, (name, func) inzip(axes.flat[:5], functions):
y = func(x)
ax.plot(x, y, 'b-', linewidth=2)
ax.axhline(0, color='gray', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
ax.axvline(0, color='gray', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
ax.set_title(f'{name}')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_ylim(-1.5, 5)
# Softmax示例
inputs = np.array([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0])
y_softmax = softmax(inputs)
ax6 = axes[1, 2]
ax6.bar(range(len(inputs)), y_softmax, color='purple', alpha=0.7)
ax6.set_title('Softmax Output')
ax6.set_xlabel('Input Index')
ax6.set_ylabel('Probability')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('activation_functions.png', dpi=150)
plt.show()
6.2 导数计算
# 计算各激活函数的导数
defsigmoid_derivative(x):
s = sigmoid(x)
return s * (1 - s)
deftanh_derivative(x):
t = tanh(x)
return1 - t**2
defrelu_derivative(x):
return np.where(x > 0, 1, 0)
# 验证导数
x = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100)
print("Sigmoid导数最大值:", max(sigmoid_derivative(x)))
print("Tanh导数最大值:", max(tanh_derivative(x)))
print("ReLU导数范围:", relu_derivative(x).min(), "~", relu_derivative(x).max())