大浩浩的笔记课堂——FRM考试学习笔记123
- 2026-02-12 04:53:26
Topic 52 Estimating Liquidity Risks
1.Liquidity and liquidity risks:
⑴liquidity:
①definition:
It is the ability of a trader to execute a trade or liquidate a position with little or no cost,risk or inconvenience.
②categories:
A.exogenous liquidity:
It refers to the bid-ask spread not being affected by the individual trades made by investors.This is more likely to be the case when the trades are relatively small.
B.endogenous liquidity:
a/ definition:
It refers to when a given trade can influence the liquidity risk of the trade.
b/ example:
a trader submitting a buy or sell order that increases the spread
③challenge:
A.The main challenge in estimating liquidity is finding the best method.
B.One approach is finding adjustments to add on to the basic VaR.The
researcher must understand how the inputs affect the ″add-on″ and if there are more than one,how the add-ons interact.
⑵liquidity risk:
①definition:
It is the lack of a market for a security to prevent it from being bought or sold quickly enough to prevent or minimize a loss.
②reason:
It could result from asset allocation,funding strategies,collateral policies,or mismanagement of risks.
③categories:
A.transaction liquidity risk:
It is the risk that the act of buying or selling an asset will result in an adverse price move.
B.balance sheet risk/funding liquidity risk:
It results when a borrower´s credit position is either deteriorating or is perceived by market participants to be deteriorating.
2.Estimating liquidity adjusted VaR:
liquidity adjusted VaR=VaR+liquidity cost(LC):
⑴exogenous price(LVaR is higher):
①constant spread approach:
A.assumption:
The bid-ask spread is constant.
B.formula:
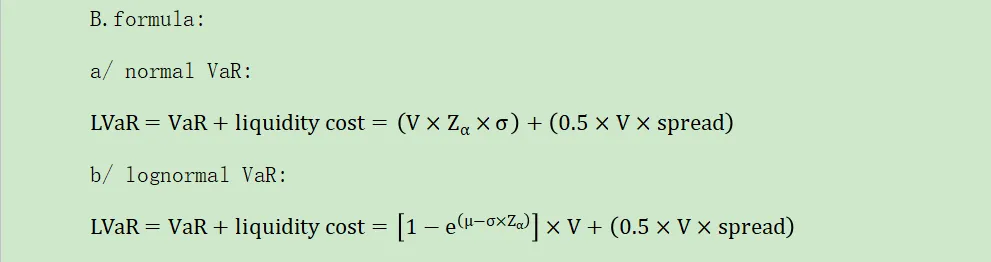
C.factors:

·特别注意!
·liquidity adjustment:

The liquidity adjustment will increase(decrease) when there is an increase(decrease) in the spread,a decrease(increase) in the confidence level,and a decrease(increase) in the holding period.
②random spread approach:
A.definition:
LVaR can also be calculated given the distributional characteristics of spread.
B.formula:
If you are given the mean and standard deviation of the spread,apply the follow:

⑵endogenousprice(LVaR is lower):
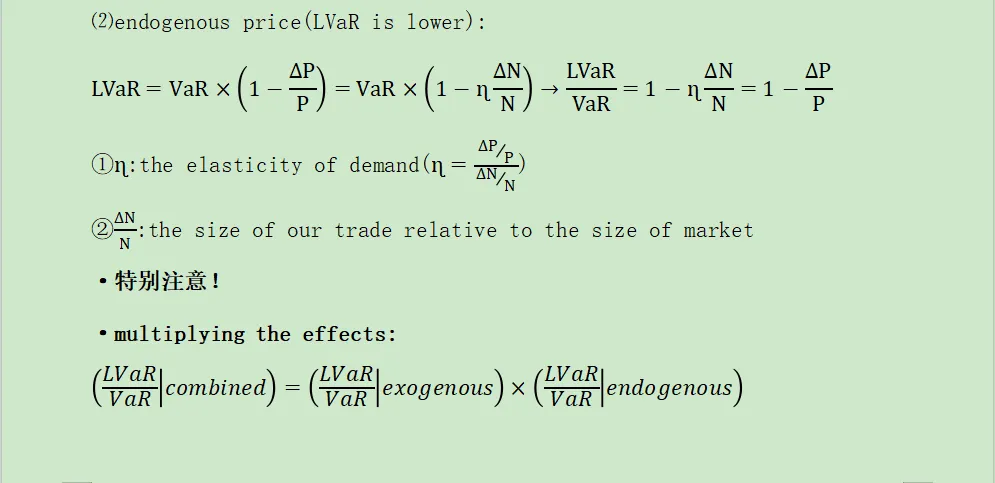
⑶the liquidity discount approach
3.Estimating liquidity-at-risk(LaR):
⑴LaR:
①another name:
It is also known as cash flow at risk(CFaR),it is the cash-flow version of VaR.
②definition:
It is the maximum likely cash outflow over the horizon period at a specified confidence level:
For a hedged portfolio,the LaR can differ significantly from the VaR:
A.A bond hedged with a futures contract has low VaR but high VaR.
B.A hedging instruments do not result in potential cash outflows over the measurement period.
③example:
The 1-day LaR at the 95% confidence means that the maximum likely cash outflow over the next day,at the 95% confidence level.
④characteristics:
A.LaR is similar to VaR,but instead of a change in value,it deals with cash flows.
B.LaR is concerned with a cash flow shortfall,VaR is concerned with a loss in value.
C.A positive(negative) value for LaR means that the worst outcome will be associated with an outflow(inflow) of cash.
⑤factors:
borrowing or lending,margin requirements,collateral obligations,unexpected cash flows,and changes in risk management policy
⑵VaR and LaR:
VaR | LaR | |
the risk | the risk of losses/profits | the risk of cash outflows |
depend on | depends largely on netted or hedged position | depends on the larger gross position |
·特别注意!
·So,the LaR can be much greater than the VaR or much less than it,depending on the circumstances.
大浩浩的笔记课堂之FRM考试学习笔记合集
【正文内容】
FRM二级考试
A.Market Risk
A.市场风险
Topic 1 Estimating Market Risk Measures:An Introduction and Overview
Topic 2 Non-Parametric Approaches
Topic 3 Parametric Approaches:Extreme Value
Topic 6 Messages from the Academic Literature on Risk Management for the Trading Book
Topic 7 Some Correlation Basics:Properties,Motivation and Terminology
Topic 8 Empirical Properties of Correlation:How Do Correlation Behave in the Real World
Topic 9 Statistical Correlation Models—Can We Apply Them to Finance
Topic 10 Financial Correlation Modeling—Copula Correlations
Topic 11 Empirical Approaches to Risk Metrics and Hedging
Topic 12 The Science of Term Structure Models
Topic 13 The Shape of the Term Structure
Topic 14 The Art of Term Structure Models:Drift
Topic 15 The Art of Term Structure Models:Volatility and Distribution
Topic 16 Overnight Index Swap(OIS) Discounting
B.Credit Risk
B.信用风险
Topic 20 Default Risk:Quantitative Methodologies
Topic 21 Credit Risks and Credit Derivatives
Topic 22 Credit and Counterparty Risk
Topic 23 Spread Risk and Default Intensity Models
Topic 25 Structured Credit Risk
Topic 26 Defining Counterparty Credit Risk
Topic 27 The Evolution of Stress Testing Counterparty Exposures
Topic 28 Netting,Compression,Resets,and Termination Features
Topic 32 Default Probability,Credit Spreads and Credit Derivatives
Topic 33 Credit Value Adjustment(CVA)
Topic 35 Credit Scoring and Retail Credit Risk Management
Topic 38 Understanding the Securitization of Subprime Mortgage Credit
C.Operational Risk
C.操作风险
Topic 39 Principles for the Sound Management of Operational Risk
Topic 40 Enterprise Risk Management:Theory and Practice
Topic 41 Observations on Developments in Risk Appetite Frameworks and IT Infrastructure
Topic 42 Operational Risk Data and Governance
Topic 45 Validating Rating Models
Topic 47 Risk Capital Attribution and Risk-Adjusted Performance Measurement
Topic 48 Range of Practices and Issues in Economic Capital Framework
Topic 49 Capital Planning at Large Bank Holding Companies
Topic 50 Repurchase Agreements and Financing
Topic 51 Assessing the Quality of Risk Measures
