大浩浩的笔记课堂——FRM考试学习笔记090
- 2026-01-10 01:35:23
Topic 19 The Credit Analyst
1.The universe of credit analysts:
⑴risk management(most):
Market risk,liquidity risk and operational risk.
⑵investment selection(small portion):
①bank examiners(heart)—fixed-income analysts(the risk of default)
②rating agency analysts—equity analysts
·特别注意!
·Both fixed-income analysts and equity analysts are performing fundamental and/or technical analysis on a day-to-day basis.
⑶the categories of analysts:
①corporate credit analysts:
A.The larger the size of the firm,the lower the cost of analysis.
B.An analyst will most likely focus on only one/two industry areas.
C.Cash flow analysis is key to assessing corporate credit risk.
②bank and financial institution analysts:
A.counterparty credit(counterparty risk/settlement risk);
B.product knowledge
·特别注意!
·The statement of cash flows is not helpful in bank credit analysis.
③sovereign/municipal credit analysts(broader risk/sovereign risk)
·特别注意!
·When analyzing the credit risk of foreign banks,analysts must place a lot of emphasis on sovereign risk.
⑷classification by employers:
①banks and related financial institutions(such as NBFIs):
banking credit analyst tasks:
A.counterparty credit analyst
B.fixed-income analyst:
determining relative value
C.equity analyst:
a/ determining ROE
b/ performing fundamental and/or technical analysis on a day to day basis
②institutional investors(including pension funds and insurance firms);
③rating agencies:
A.rating system:
A good rating system has 3 key features:
a/ objectivity and homogeneity:
Producing judgements tied solely to credit risk and ratings that are comparable across market segments,portfolios and customer types.
b/ specificity:
Accurately capturing the distance to default while ignoring other non-default-related financial elements.
c/ measurability and verifiability:
Providing accurate expectations tied to default probabilities backtested on a continuous basis.
B.the 3 major global agencies:
a/ Moody´s Investor Services
b/ Standard&Poor´s Rating Services
c/ Fitch Ratings
C.credit rating critical in:
a/ Borrowers can access capital markets.
b/ The various risks of value creation are appropriately managed.
c/ The economic performance of business units can be compared.
D.rating assignment methodologies:
a/ experts-based approaches:
△They rely on experienced individuals who can provide valuable inputs in to the models.
△Agency ratings are deemed more compliant then internal.
b/ statistical-based models:
Using both quantitative and qualitative data to describe the real world in a controlled environment.
c/ numerical methods:
△They are designed to derive optimal solutions using trained algorithms.
△They are called "neural network" due to continuously learning by experiences.
△Reaching optimal solutions adopting "trained" algorithms to take decisions in highly complex environments.
d/ agencies´ ratings:
In terms of the 3 features of a good rating system,agencies´ ratings are considered more compliant than internal experts-based ratings.
e/ structural approaches:
△They are based on economic and financial theoretical assumptions that describe the overall path to default.
△They involve building a model that estimates the formal relationships linking relevant model variables.
△e.g.the Merton model
f/ reduced form approaches:
△Using the most statistically suitable set of variables and disregarding the theoretical and conceptual causal relations.
△They are heavily depend on the samples chosen.
△e.g.statistical-based models & numerical methods
g/ linear discriminant analysis(LDA):
△It is used to develop scoring models to provide accept/reject decisions.
△the cutoff score:
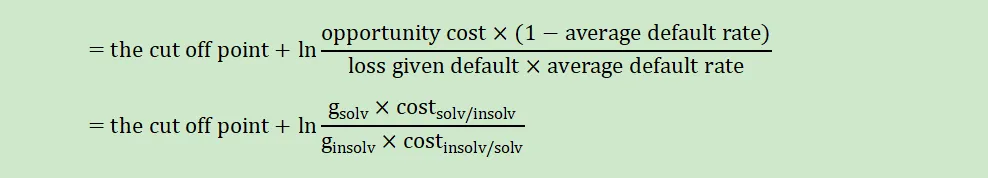
△the higher the cutoff score,the better the rating.
h/ logic regression(LOGIT) models:
△definition:
·They are tools used to predict default based on understanding the relationships between dependent and independent variables.
·The individual models developed are integrated using either a parallel or sequence approach into a final rating model.
△formula:

△characteristic:
They are generalized liner model(GLM),which is including systematic component,random component and link function.
△component:
ratings+default probabilities
△challenges:
·model risk;
·cost for building,and monitoring model;
·accurately defining default
i/ cluster analysis:
△It aggregates and segments borrowers based on the profiles of their variables.
△It is including hierarchical clustering and divisive clustering.
j/ principal component analysis:
It takes original data and transforms it into a new derived data set,which is used to determine the primary drivers of a firm´s profile and potential default.
k/ factor analysis:
It is often used as the second stage of principal component analysis.
l/ canonical correlation method:
Addressing the correspondence between a set of independent variables and a set of dependent variables.
m/ cash flow analysis:
△It is useful for assigning ratings to companies that don´t have
meaningful historical data for predicting potential default.
n/ heuristic methods:
△They are opposed to algorithms-based approaches,as "expert systems" based on artificial intelligence techniques.
△They learn both successes and errors.
④government agencies;
⑤organization of the credit risk function within banks
2.Credit analysis:
tools and methods:
⑴the usual course of events,the analyst will:
Gather information→distill the data→compare the data with peers and past performance→reach conclusions
⑵qualitative and quantitative aspects(equally important):
①elements:
A.quantitative elements(ratio analysis):
objective,ability:
a/ management´s education&experience;
b/ internal controls associated with financial reporting;
c/ diversification of products and customers locally&globally
B.qualitative elements(concerning those which can not be directly reduced to numbers):
subjective,willingness:
trends in through put and other operational efficiency metrics
②intermingling
⑶different analysis:
①macro and micro analysis;
②peer analysis:
E.g.comparison of a subject bank to similar banks and financial institutions
③research skills:
A.research types:
primary research(its high cost) and secondary research
B.research skills:
a/ primary research skill:
detailed review,in analyzing an unfamiliar banking sector
b/ secondary research skill
⑷resources:
①trade-offs in:
Annual reports,interim financial statements,financial data sources,news services,rating agency reports and other third-party research,prospectuses and offering circulars,notes from the bank visit/third parties.
·特别注意!
·The bank visit is practically a prerequisite for the rating agency analyst.
②limited resources:
In general,the rating agency analyst will engage in primary research to a greater extent while the counter-party credit analyst will depend more heavily on secondary research sources.
⑸steps:
primary research→detailed review(such as in analyzing an unfamiliar banking sector)
3.Requisite data for the bank credit analysis:
⑴the annual report;
⑵the auditor´s report or statement:
①content and meaning of the auditor´s opinion:
A.a clean or unqualified opinion 无保留意见:
The auditor has attached no additional conditions to its opinion,or the opinion is without further qualification.
B.qualified opinion 保留意见:
The auditor limits or qualifies in some way their opinion that the financial statements,it provides a fair representation of the bank´s financial condition.
②change in auditors:
It should be noted for possible further inquiry.
③who is the auditor?
⑶financial statements or reporting:
①4 primary financial statements:
A.the balance sheet(include off-balance-sheet items)
B.the income statement
C.the statement of cash flows
D.the statement of changes in capital funds
②timeliness of financial reporting:
At best,publication of annual reports will follow within one to two months following the end of the financial year.
⑷bank´s website;
⑸news,the internet,securities pricing data;
⑹prospectuses and regulatory fillings;
⑺raging agency reports and other third-party research
大浩浩的笔记课堂之FRM考试学习笔记合集
【正文内容】
FRM二级考试
A.Market Risk
A.市场风险
Topic 1 Estimating Market Risk Measures:An Introduction and Overview
Topic 2 Non-Parametric Approaches
Topic 3 Parametric Approaches:Extreme Value
Topic 6 Messages from the Academic Literature on Risk Management for the Trading Book
Topic 7 Some Correlation Basics:Properties,Motivation and Terminology
Topic 8 Empirical Properties of Correlation:How Do Correlation Behave in the Real World
Topic 9 Statistical Correlation Models—Can We Apply Them to Finance
Topic 10 Financial Correlation Modeling—Copula Correlations
Topic 11 Empirical Approaches to Risk Metrics and Hedging
Topic 12 The Science of Term Structure Models
Topic 13 The Shape of the Term Structure
Topic 14 The Art of Term Structure Models:Drift
Topic 15 The Art of Term Structure Models:Volatility and Distribution
Topic 16 Overnight Index Swap(OIS) Discounting
B.Credit Risk
B.信用风险
