大浩浩的笔记课堂——FRM考试学习笔记124
- 2026-02-12 20:50:52
Topic 53 Liquidity and Leverage
1.Liquidity and liquidity risk:
⑴liquidity
①transaction liquidity:
It is the property of an asset being easy to exchange for other assets.
②funding liquidity:
It is the ability to finance assets continuously at an acceptable borrowing rate.
⑵liquidity risk:
①transaction liquidity risk:
A.definition:
It is the risk of moving the price of an asset adversely in the act of buying or selling it.
B.related:
It is fundamentally related to the costs of searching for a counterparty,the institutions required to assist in that search,and the costs of including a counterparty to hold a position.
C.characteristics:
a/ It is low if assets can be liquidated or a position can be covered quickly,cheaply,and without moving the price too much.
b/ The lack of a market for a security to prevent it from being bought or sold quickly enough to prevent or minimize a loss.
②balance sheet risk/funding liquidity risk:
A.definition:
It is the risk that creditors either withdraw credit or change the term on which it is grated in such a way that the positions have to be announced and/or no longer profitable.
B.related:
It is related to individual´s or firm´s creditworthiness.
·特别注意!
·Transaction liquidity risk and balance sheet risk/funding liquidity risk are the two types interact:
Risks associated with liquidity are interrelated and can exacerbate problems.For example,an increase in funding liquidity risk can lead to an increase in transactions liquidity risk.Also,severe stress to the financial system from a liquidity risk event could impact market participants simultaneously,suggesting that the illiquidity or insolvency of one counterparty may impact other market participants.
③systemic risk:
It is the risk of a general impairment of the financial system,usually in situations of severe financial stress.
2.Transactions liquidity risk:
⑴causes of transactions liquidity risk:
①cost of trade processing
②inventory management by dealers
③adverse selection
④difference of opinion
⑵factors influence transaction liquidity:
①number of traders in the market
②frequency and size of trades
③time it takes to carry out a trade
④cost of transacting
⑤exchange-traded positions(having more liquid markets than OTC)
⑥the type of asset and the degree to which the asset is standardized
⑶characteristics of market liquidity:
①tightness:
It is the cost of a round-trip transaction and is typically measured by the bid-ask spread and brokers´commissions.
②depth:
It is the how large an order it takes to move the market adversely.
③resiliency:
It is the length of time for which a humpy order moves the market away from the equilibrium price.
·特别注意!
·Lack of liquidity manifests itself in these observable:
*bid-ask spread:
A wider(narrower) bid-ask spread indicates lower(higher) liquidity.If an asset becomes less liquid,the spread increases,and the costs of trade the asset increases.
*adverse price impact;
*slippage:
When the price deteriorates in the time,it takes to get a trade done.
3.Balance sheet risk/Funding liquidity risk:
⑴maturity transformation:
①maturity mismatch:
It is the longer-term asset with shorter-term liability.
②net interest margin:
net interest margin=the interest they earn-funding cost
③rollover risk(cliff risk):
It is the risk that the short-term debt can not be refinanced.
⑵liquidity transformation:
The money market instruments are short-term interbank,commercial paper of creditworthy issuers,repos with haircuts,government bills.
⑶commercial banking:
①liquidity transformation by banks:
Turning illiquid assets into liquid ones:
assets | liabilities |
cash and government bonds $15 million | common equity $10 million |
5-year corporate loans $85 million | Deposits $90 million |
②fragility of commercial banking:
A.bank categories:
a/ fractional-reserve bank:
Banks only expect a fraction of deposits and other liabilities to be redeemed at any point in time.As a result,they do not hold all deposits in liquid assets,but make loans with deposits instead.
b/ 100 percent reserve bank
B.bank run 挤兑:
a/ higher capital to reduce the concern about solvency
b/ higher reserves to reduce the concern about liquidity
C.rollover risk 延期付款
③asset-liability management(AML):
It is the process of using deposits to finance loans,keeping certain ratios of ready cash and readily marketable securities to meet unusual demands by depositors and other short-term lenders.
⑷structured credit and off-balance-sheet funding:
off-balance-sheet vehicles:
①asset-backed commercial paper(ABCP) conduits→issue ABCP
②structured investment vehicles(SIVs)→issue ABCP+MTM
⑸funding liquidity of other intermediaries:
①extreme position(repay instantly or demand):
depository institutions and money market mutual funds(MMMFs)
②securities firms;
③hedge funds:
A.categories:
a/ LBOs:
They are generally financed by large loans,called leveraged loans.
b/ merger arbitrage hedge fund:
Mergers typically result in an increase in the target acquisition price and in a decrease in the acquirer´sprice.
·特别注意!
·The merger arbitrage hedge fund are experienced large losses in late 2007 and early 2008 because the abandoned merger plans due to lack of available financing.
c/ convertible arbitrage:
Prices are often only slightly lower than their theoretical prices based on the replicating portfolio of plain-vanilla equity options and bonds.
B.ways:
Hedge funds manage liquidity via
a/ cash
b/ Unpledged assets are assets not currently being used as collateral.
c/ unused borrowing capacity:
This is not an unfettered source of liquidity.
C.market stress:
In times of market stress,redemption requests may require hedge fund managers to unwind positions rapidly,exposing the fund to transactions liquidity risk.If this happens to many funds at once,fire sales may result.
④money market mutual funds(MMMFs):
A.liquidity:
The assets can still fluctuate in value,so the ability to offer unlimited instantaneous withdrawals is potentially limited if asset value fall.
B.characteristics:
a/ Do not have to be marked-to-market(MTM) each day.
b/ The values of the underlying assets in the fund are subject to change.
c/ They have net asset value equal to $1.00.However,credit write-downs can result in net asset values(NAVs) falling below $1.00.This is known as breaking the buck.Liquidity risk can also cause NAVs to fall below $1.00.
⑹systematic funding liquidity risk:
①The funding liquidity risk in corporate transactions is both
idiosyncratic and systematic.
②Hedge funds experienced large losses as mergers were abandoned then financing dried up.
4.Liquidity risk measurement:
⑴measuring transaction liquidity risk:
①the available data:
A.bid-ask data
B.transaction or turn over data
C.data on the size outstanding of securities issues
②transaction cost liquidity risk formula:

③measuring the risk of adverse price impact:
A.liquidity-adjusted VaR
B.financial crisis may be due to the trade off among adverse impact,funding liquidity or solvency.
C.Liquidation decisions may also interact with the incentive structure of credit markets.
⑵measuring funding liquidity risk:
①asset-liability management(ALM):
Keeping cash,or cash equivalents on hand.
②funding liquidity management for hedge funds:
A.cash(U.S.Treasures)
B.unpledged assets
C.unsecured borrowing capacity
③indicators of liquidity risk:
A.term spread:
It is the difference between LIBOR and Fed funds.
B.TED spread:
It is the credit spread between Eurodollar LIBOR and Treasuries.
C.rapid asset growth:
It is a warning indicator.
5.The collateral market:
⑴collateral tools:
①margin loans:
A.definition:
Financing a security transaction in which the loan is collateralized by the security.
B.margin call:
If the market value of long position declines,the broker loses the protection.
C.margin lending:
It is used by investors wishing to take leveraged long positions in securities.
②repurchase agreements:
A.They are matched pairs of the spot sale and forward repurchase of security.
B.Reverse repo transactions are financing long positions in securities,typically bonds.
③securities lending:
A.One party lends a security to another in exchange for a fee,called a rebate.
B.The security lender continues to receive dividend and interest cash flows from the security.
④total return swaps:
One party pays a fixed fee and receives the total return on a specified equity position on the other.
⑵collateral element:
①A crucial element in permitting bonds to serve as collateral is their credit quality.
②The utility of high-quality bonds as collateral adds to the value of securitized credit products.
③Collateralized loans are used to finance securities or other assets or trades.The securities pledged to one firm are often loaned or pledged again,hence the collateral circulates.This process is known as rehypothecation or repledging.
⑶collateral market:
①firms:
Firms with excess cash are more willing to lend at a low rate of interest if the loan is secured by collateral.The full value of the securities is not lent,the difference is called a haircut.
②agencies:
Credit-rating agencies are important participants in collateral markets.
③markets:
A.Collateral markets bring owners of securities such as institutional investors and insurance companies into the financing markets.
B.Collateral markets enhance the ability of firms to borrow money.They also make it possible to establish short positions in securities.Cash and securities may be borrowed in the market for collateral.
6.Leverage and forms of credit in contemporary finance:
⑴defining and measuring leverage:
①leverage ratio:
A.definition:
It is a firm´s leverage ratio is equal to its assets divided by equity.
B.formula:
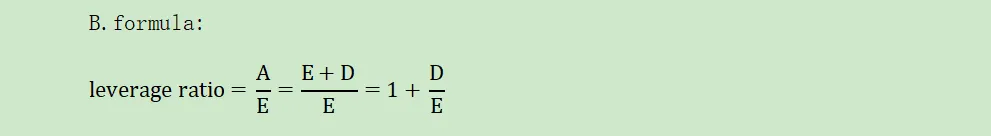
②leverage effect:
Return on equity(ROE) is higher as leverage increases,as long as the firm´sreturn on assets(ROA) exceeds the cost of borrowing funds.
③ROE formulas:
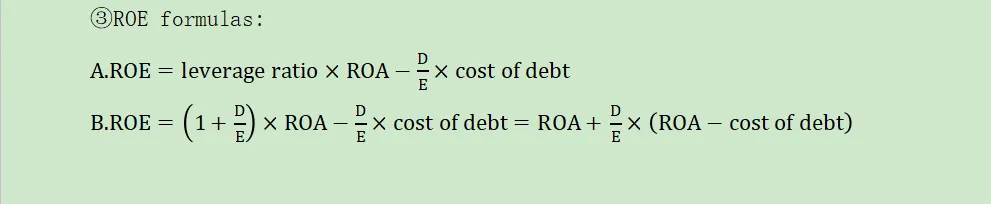
⑵margin loans and leverage:
The leverage on a position with a haircut of h is 1/h.
·特别注意!
·There is embedded leverage in short positions and derivatives such as options and swaps.Economic balance sheets can be constructed to help investors and/or firms measure the implicit leverage of these transactions.
大浩浩的笔记课堂之FRM考试学习笔记合集
【正文内容】
FRM二级考试
A.Market Risk
A.市场风险
Topic 1 Estimating Market Risk Measures:An Introduction and Overview
Topic 2 Non-Parametric Approaches
Topic 3 Parametric Approaches:Extreme Value
Topic 6 Messages from the Academic Literature on Risk Management for the Trading Book
Topic 7 Some Correlation Basics:Properties,Motivation and Terminology
Topic 8 Empirical Properties of Correlation:How Do Correlation Behave in the Real World
Topic 9 Statistical Correlation Models—Can We Apply Them to Finance
Topic 10 Financial Correlation Modeling—Copula Correlations
Topic 11 Empirical Approaches to Risk Metrics and Hedging
Topic 12 The Science of Term Structure Models
Topic 13 The Shape of the Term Structure
Topic 14 The Art of Term Structure Models:Drift
Topic 15 The Art of Term Structure Models:Volatility and Distribution
Topic 16 Overnight Index Swap(OIS) Discounting
B.Credit Risk
B.信用风险
Topic 20 Default Risk:Quantitative Methodologies
Topic 21 Credit Risks and Credit Derivatives
Topic 22 Credit and Counterparty Risk
Topic 23 Spread Risk and Default Intensity Models
Topic 25 Structured Credit Risk
Topic 26 Defining Counterparty Credit Risk
Topic 27 The Evolution of Stress Testing Counterparty Exposures
Topic 28 Netting,Compression,Resets,and Termination Features
Topic 32 Default Probability,Credit Spreads and Credit Derivatives
Topic 33 Credit Value Adjustment(CVA)
Topic 35 Credit Scoring and Retail Credit Risk Management
Topic 38 Understanding the Securitization of Subprime Mortgage Credit
C.Operational Risk
C.操作风险
Topic 39 Principles for the Sound Management of Operational Risk
Topic 40 Enterprise Risk Management:Theory and Practice
Topic 41 Observations on Developments in Risk Appetite Frameworks and IT Infrastructure
Topic 42 Operational Risk Data and Governance
Topic 45 Validating Rating Models
Topic 47 Risk Capital Attribution and Risk-Adjusted Performance Measurement
Topic 48 Range of Practices and Issues in Economic Capital Framework
Topic 49 Capital Planning at Large Bank Holding Companies
Topic 50 Repurchase Agreements and Financing
Topic 51 Assessing the Quality of Risk Measures
Topic 52 Estimating Liquidity Risks
