有限元基础学习笔记(三)
- 2026-02-09 19:48:02
从公式到代码:1D 有限元 Python 实现
本文我们用 Python 写一个最小 1D 有限元求解 demo,来帮助理解前面推导的公式。
在 FEM 代码里,最机械但关键的工作只有一件事:把弱形式里的积分算出来。
为此需要两块铺垫:等参元 与 高斯积分。
1. 等参元与数值积分
弱形式中最常见的两类积分项(以 1D 杆单元为例)是:
其中, , , 可能随着 变化,积分往往难以解析求出,因此需要数值积分。
1. 高斯积分(Gauss quadrature)
高斯积分 的思想是:把 上的积分用若干采样点的加权求和近似:
其中 是权重,是高斯积分点。
实际问题里,每个单元的积分区间一般是 ,如果直接在 上布置积分点,代码会变得很碎,因为每个单元长度不同,坐标不同,积分点位置也不同。
所以 FEM 通常会先做 等参映射:把所有单元都搬到同一个参考区间 。
2. 等参元(Isoparametric element)
等参元 的思路是:
• 把每个物理单元 都映射到同一个参考单元 。
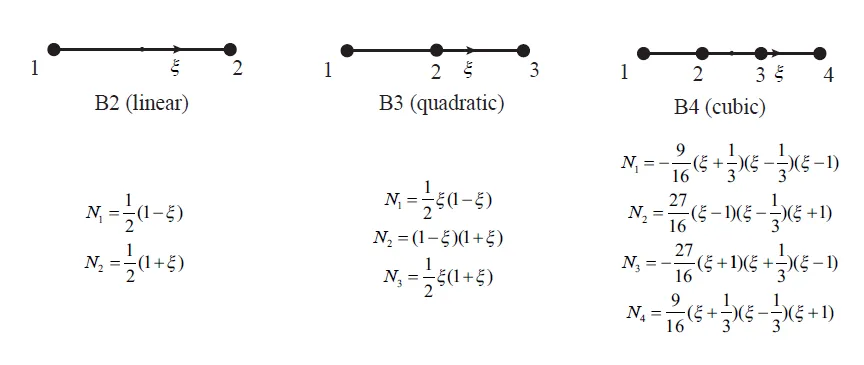
以二阶三节点单元为例,我们用形函数插值几何坐标:
对 求导:
因此微分关系是:
其中 是 Jacobian(1D为标量)
弱形式里的刚度矩阵需要 ,但形函数天然写在 ,所以要用链式法则把导数换回物理坐标:
3. 任意积分的统一计算
有了等参映射以后,任何 上的积分都能写成:
再用高斯积分得到计算公式:
4.选几个高斯点?
点Gauss–Legendre在上对次数的多项式积分是精确的
实际 FEM 里高斯点个数的选择,取决于你要积分的被积函数最高有多复杂。
经验上可以这样取:
• 刚度矩阵:若 , 在单元内近似常数,线性单元用 1 点即可。 • 体力项:如果 至少是线性的,线性单元通常需要 2 点才能算准。 • 高阶单元一般取 较为合适。
2. 1D 有限元 Python 代码
有限元代码的核心任务是:
计算单元矩阵与向量 → 组装整体方程 → 施加边界条件 → 求解。
本 demo 以之前的 1D 杆问题为例,实现:
• 自定义等分网格 • 自定义单元阶次 • 计算出未知节点位移 • 生成位移场 及应力场
1. 问题描述(problem.py)
仍取前面推文中的案例,具体参数:
• 杆长 , 为常数 • 体力 (或 ) • 左端 :自然边界 • 右端 :本质边界
E = 100000.0
A = 1.0
def q(x):
return 10.0 * A * x
natural_bcs = {0.0 : 10.0}
essential_bcs = {2.0 : 0.0}2. 网格(mesh.py)
等分网格要输出两样东西:
• coords: 全局节点坐标• conn: 每个单元包含哪些节点(连通性)
对 阶单元,单元间共享端点,所以总节点数:
import numpy as np
def make_mesh_1d(x0, xl, nel, p):
"""
x0: float,起点坐标
x1: float,终点坐标
nel: int,单元数
p: int,单元阶数
"""
nnp = nel * p + 1
coords = np.linspace(x0, xl, nnp)
conn = np.zeros((nel, p+1), dtype=int)
for e in range(nel):
conn[e, :] = np.arange(e * p, e * p + (p + 1))
return coords, conn3. 单元形函数(shape1d.py)
等参坐标 ,等距节点:
Lagrange 形函数:
导数:
def lagrange_shape_1d(p, xi):
"""
输入:
p: int,单元阶数
xi: 等参元坐标,在[-1,1]范围上
----------
输出:
N: (p+1, ) xi为输入时的形函数值
dN_dxi: (p+1, ) xi为输入时形函数一阶导数值
"""
N = np.ones(p+1, dtype=float)
dN_dxi = np.zeros(p+1, dtype=float)
xii = np.zeros(p+1, dtype=float)
### 对应公式Eq.9
for i in range(p+1):
xii[i] = -1 + 2 * i / p
### 对应公式Eq.10
for i in range(p+1):
for j in range(p+1):
if i != j:
N[i] = N[i] * (xi - xii[j]) / (xii[i] - xii[j])
### 对应公式Eq.11
for i in range(p+1):
term = 0
for k in range(p+1):
if k != i:
prod = 1
for j in range(p+1):
if (j != k) and (j != i):
prod = prod * (xi - xii[j]) / (xii[i] - xii[j])
term += (1/(xii[i] - xii[k])) * prod
dN_dxi[i] = term
return N, dN_dxi4. 数值积分(quad.py)
最小实现:1~3 高斯点,后续可补充。
def gauss_legendre(n_gauss):
"""
输入:
n_gauss: int,高斯积分点
----------
输出:
xi_g: (n_gauss, ) 对应的高斯点坐标
w_g: (n_gauss, ) 对应的权重
"""
xi_g = np.zeros(n_gauss)
w_g = np.zeros(n_gauss)
if n_gauss == 1:
w_g[0] = 2.0
xi_g[0] = 0.0
elif n_gauss == 2:
xi_g[:] = [-0.5773502691896257, 0.5773502691896257]
w_g[:] = [1.0, 1.0]
elif n_gauss == 3:
xi_g[:] = [-0.7745966692414834, 0.0, 0.7745966692414834]
w_g[:] = [0.5555555555555556, 0.8888888888888888, 0.5555555555555556]
else:
raise ValueError("n must be 1, 2, or 3 in this demo.")
return xi_g, w_g5. 单元矩阵与向量(element1d.py)
单元积分统一写成参考单元 上的求和:
每个高斯点的计算顺序很固定:
Step 1 形函数与导数:
Step 2 物理坐标:
Step 3 Jacobian:
Step 4 矩阵:
Step 5 累加 :
Step 6 累加 :
import numpy as np
from quad import *
from shape1d import *
from problem import *
def element_matrices(coords_e, p, n_gauss):
"""
输入:
coords_e: 单元物理坐标
p: 单元阶次
n_gauss: 高斯点个数
----------
输出:
Ke: (p+1, p+1) 单元刚度矩阵
fe: (p+1, ) 单元外荷载向量
"""
nen = p+1 # 单元节点数
Ke = np.zeros((nen, nen))
fe = np.zeros(nen)
xi_g, w_g = gauss_legendre(n_gauss)
for i in range(n_gauss):
xi = xi_g[i]
w = w_g[i]
# Step 1: N, dN/dxi
N, dN_dxi = lagrange_shape_1d(p, xi)
# Step 2: x(xi)
x = N @ coords_e
# Step 3: J(xi)
J = dN_dxi @ coords_e
# Step 4: B = dN/dx
dN_dx = dN_dxi / J
B = dN_dx
# Step 5: Ke
Ke += (E*A) * np.outer(B, B) * (w * J)
# Step 6: fe (body force)
fe += N * q(x) * (w * J)
return Ke, fe6. 组装与求解(solver1d.py)
组装整体矩阵
前面刚好有一个变量 conn 定义是的各单元内节点的编号。
import numpy as np
from mesh import *
from element1d import *
from problem import *
def assemble_global(coords, conn, p, n_gauss):
"""
输入:
coords: 所有节点物理坐标
conn: 各单元上的节点ID
p: 单元阶次
n_gauss: 高斯点个数
----------
输出:
K: (ndofs, ndofs) 整体刚度矩阵
f: (ndofs, ) 整体外荷载向量
"""
ndofs = coords.shape[0] # 总自由度
nele = conn.shape[0] # 总单元数
K = np.zeros((ndofs, ndofs))
F = np.zeros(ndofs)
for e in range(nele):
edofs = conn[e, :] # 各单元内自由度编号,如[0, 1, 2]
coords_e = coords[edofs]
ke, fe = element_matrices(coords_e, p, n_gauss)
for i in range(p+1):
F[edofs[i]] += fe[i] #单元e中第i个自由度在整体中的编号edofs[i]
for j in range(p+1):
K[edofs[i], edofs[j]] += ke[i, j]
return K, F施加边界条件并求解
这里做两件事:
• 自然边界 加到载荷向量 F 上 • 本质边界 通过分块消元求解未知自由度
本 demo 只处理每类 BC 各 1 个的情况。
对 按照自由度进行分块得:
通过第二行公式来求解未知位移:
def apply_bcs_and_solve(K, F, coords):
"""
输入:
K: (ndofs, ndofs) 整体刚度矩阵
F: (ndofs, ) 整体外荷载向量
coords: (ndofs, ) 所有节点坐标
----------
输出:
d: (ndofs, ) 整体节点位移
"""
ndofs = K.shape[0]
# 施加自然边界条件(牵引力)
x_t = list(natural_bcs.keys())[0]
tbar = natural_bcs[x_t] * A
node_t = np.where(np.isclose(coords, x_t))[0][0] #vaule
F[node_t] += tbar
# 施加本质边界条件(位移)
x_u = list(essential_bcs.keys())[0] # list
ubar = essential_bcs[x_u]
fixed = np.where(np.isclose(coords, x_u))[0] #分块,本质边界条件节点id的list
fixed_set = set(fixed.tolist())
free = np.array([i for i in range(ndofs) if i not in fixed_set], dtype=int) # 分块,其他节点id的list
# 分块矩阵
K_FF = K[free][:, free]
K_FE = K[free][:, fixed]
F_F = F[free]
# 施加本质边界条件(位移)
d_E = np.array([ubar], dtype=float)
# 求解得未知节点位移
rhs = F_F - K_FE @ d_E
d_F = np.linalg.solve(K_FF, rhs)
d = np.zeros(ndofs)
d[fixed] = d_E
d[free] = d_F
return d后处理
在每个单元 上取若干采样点 ,计算:
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
def evaluate_uh_on_mesh(coords, conn, p, d, nplot_per_elem=50):
"""
输入:
coords: 所有节点物理坐标
conn: 各单元上的节点ID
p: 单元阶次
d: 所有节点位移
nplot_per_elem: 每个单元上采样点
----------
输出:
x_h, u_h, eps_h, sigma_h: 全场结果
"""
nel = conn.shape[0]
xi_grid = np.linspace(-1.0, 1.0, nplot_per_elem)
X_all, U_all, EPS_all, SIG_all = [], [], [], []
for e in range(nel):
# 每个单元上的节点id
enodes = conn[e, :]
coords_e = coords[enodes] # (p+1,)
de = d[enodes] # (p+1,)
xi_use = xi_grid
for xi in xi_use:
# 形函数及一阶导数
N, dN_dxi = lagrange_shape_1d(p, xi)
# 等参变换 Step 1
x = N @ coords_e # 每个单元采样点对应的物理坐标
J = dN_dxi @ coords_e
# 位移 Step 2
u = N @ de
X_all.append(x)
U_all.append(u)
# dN/dx = (dN/dxi)/J
dN_dx = dN_dxi / J
# 应变和应力 Step 3 and 4
eps = dN_dx @ de
sig = E * eps
EPS_all.append(eps)
SIG_all.append(sig)
x_h = np.array(X_all, dtype=float)
u_h = np.array(U_all, dtype=float)
eps_h = np.array(EPS_all, dtype=float)
sigma_h = np.array(SIG_all, dtype=float)
return x_h, u_h, eps_h, sigma_h3. 案例计算
有以上代码后,我们可以在main.py里创建一个函数用于计算。
import numpy as np
from problem import *
from mesh import *
from shape1d import *
from quad import *
from element1d import *
from solver1d import *
def run_case(x0, x1, nel, p, n_gauss, nplot_per_elem=50):
coords, conn = make_mesh_1d(x0, x1, nel, p)
K, F = assemble_global(coords, conn, p, n_gauss)
d = apply_bcs_and_solve(K, F, coords)
x_plot, u_h, eps_h, sigma_h = evaluate_uh_on_mesh(
coords, conn, p, d, nplot_per_elem=nplot_per_elem
)
return x_plot, u_h, sigma_h然后可以自定义nel, p, n_gauss这三个参数。我们先固定单元数,比较不同的p 和 n_gauss:
1. nel=2,p=1,n_gauss=12. nel=2,p=1,n_gauss=23. nel=2,p=2,n_gauss=24. nel=2,p=3,n_gauss=3
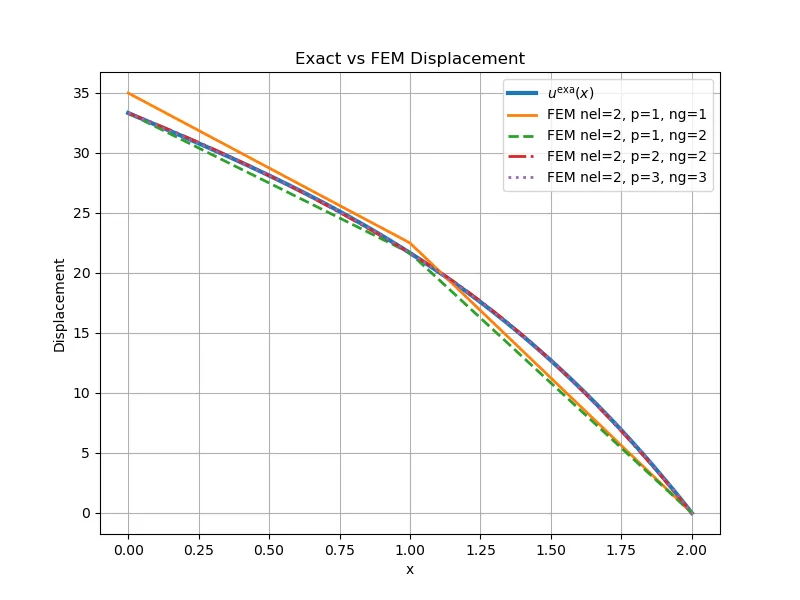
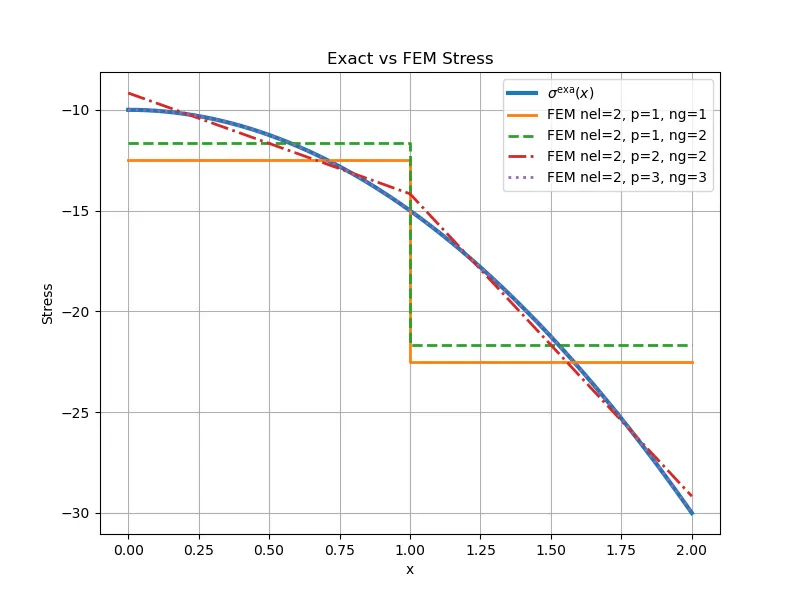
可以看出:
• 1 与 2 的位移不重合,其主要原因来自体力项积分:本例中 是线性的,线性单元 是一次,因此被积函数最高为二次,1 点Gauss 不能精确积分二次项。改用 2 点后明显改善。 • 3 与 4(高阶单元)位移更接近精确解:高阶单元在单元内允许更高次数的位移多项式,自然更容易拟合精确位移曲线。 • 应力只有 4 更贴近精确解:三次单元位移是三次多项式,因此应变/应力是二次多项式,能更好逼近本例精确应力。
进一步,固定单元阶数和高斯积分点,我们变化单元数:
5. nel=5 ,p=1, n_gauss=1
6. nel=10 ,p=1, n_gauss=1
以下为计算结果:
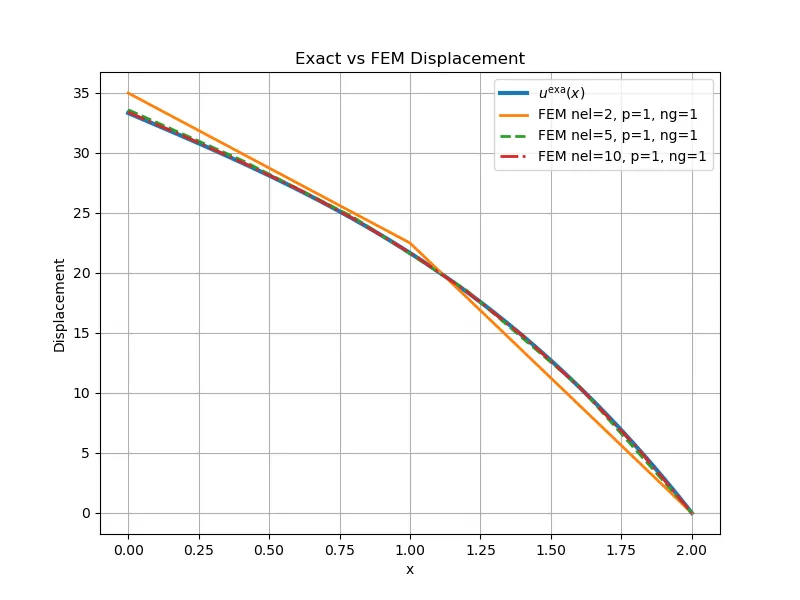
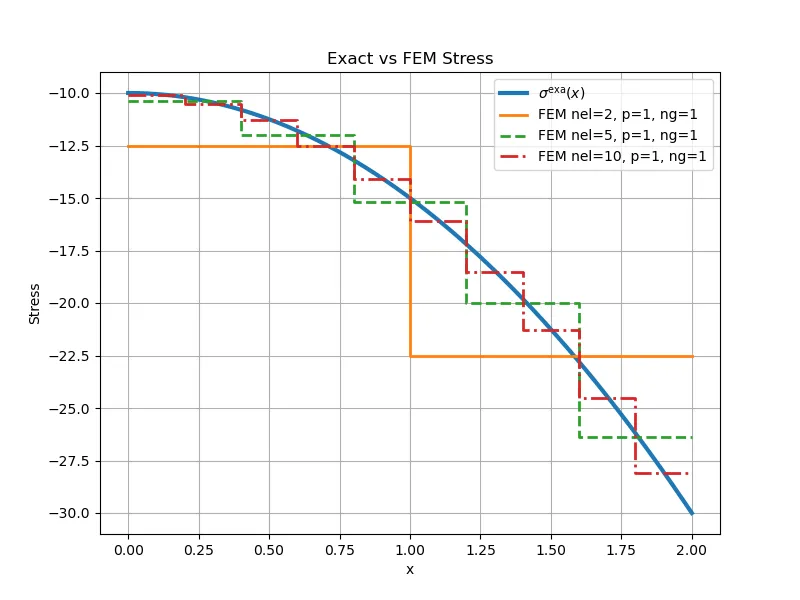
可以看出:
• 当我们增加单元数时,位移会逐步收敛到精确解。 • 但 在每个线性单元内恒为常数,所以应力曲线必然是“阶梯状”。加密网格只能让阶梯更细,并不会让它真正变光滑。想得到更光滑、更准确的应力分布,通常需要用高阶单元或应力恢复。
